Proteomic study of salt tolerant cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. BHUAR002 isolated from Usar soil
Abstract
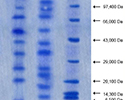
Salt stress leads to an alteration in protein profile and induction of stress-specific proteins. The SDS – PAGE analysis of total soluble proteins of Anabaena sp. BHUAR002 (Accession no. bankit1353506 HM235817) exposed to 500 mM NaCl for 24 h revealed inhibition of host proteins, induction of selected proteins and appearance of some new proteins. In view of the appreciable alteration in total soluble protein profile after 500 mM salt treatment for 24 h, this dose was selected for further physiological, biochemical and proteomic analysis of the response of Anabaena sp. BHUAR002 to salinity and to examine the relationship between these responses. Further, 2DE of the total soluble protein of Anabaena sp. BHUAR002 showed 73 spots present only in control, 43 spots present only in stress and 15 differentially expressed spots present in both control and stress but show different levels of expression. This may be due to disturbance of cellular homeostasis by salt stress. Out of fifteen, Six spots were identified after MALDI-TOF MS analysis were identified as Manganese and iron Superoxide dismutase [Anabaenavariabilis ATCC 29413], Cytidine deaminase [Porphyromonas venonis 60-3], Phycobilisome Protein [Nodularia Spumigena CCY9414], DNA replication and repair protein recF [Yersinia aldovae ATCC35236], IS1112 transposase [Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae PXO99A] and TP901 family phage tail tape measure protein [Xanthobacter autotrophicus Py2].
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Acea MJ, Prieto-Fernandez A, & Diz-Cid, N. “Cyanobacterial inoculation of heated soils: effect on microorganisms of C and N cycles and on chemical composition in soil surface.” Soil. Biol. Biochem 35 (2003): 513-524.
Apte SK and Bhagwat AA. “Salinity-stress-induced proteins in two nitrogen-fixing Anabaena strains differentially tolerant to salt.” J. Bacteriol 171(1989): 909-915.
Cabiscol E, Tamarit J and Ros J. “Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by reactive oxygen species.” Internatl. Microbiol 3 (2000): 3-8.
Chen WJ and Zhu T. “Networks of transcription factors with roles in environmental stress response.” Trends Plant Sci 9(2004): 591-596.
Davis BJ. “Disc Electrophoresis 2, method and application to human serum proteins.” Ann. New York Acad. Sci 121(1964): 404-427.
Duché O, Trémoulet F and Namane A. “The European Listeria Genome Consortium and Labadie J. A proteomic analysis of salt stress response of Listeria monocytogenes.” FEMS Microbiol Let 215(2002): 183-188.
Durner J and Böger P. “Ubiquitin in prokaryote Anabaena variabilis.” J. Biol. Chem 270(1995). :3720-3725.
Ehling-Schulz M, Schulz S, Wait R, Gorg A, and Scherer S. “The UV-B stimulon of the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc commune comprises early shock proteins and late acclimation proteins.” Mol. Microbiol 46(2002): 827-843.
Ferianc P, Farewell A, and Nystrom T. “The cadmium-stress stimulon of Escherichia coli K-12.” Microbiology 144(1998): 1045-1050.
Fulda S, Huang F, Nilsson F, Hagemann M and Norling B. “Proteomics of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 identification of periplasmic proteins in cells grown at low and high salt concentrations.” Eur. J. Biochem 267(2000): 5900-5907.
Fulda S, Huckauf J, Schoor A, and Hagemann M. “Analysis of stress responses in the cyanobacterial strains Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, and Synechococcus sp. PCC 7418: osmolyte accumulation and stress protein synthesis.” J Plant Physiol 154(1999): 240-249.
Grune T, Blasig IE, Sitte N, Roloff B, Haseloff R, and Davies KJA. “Peroxynitrite increases the degradation of aconitase and other cellular proteins by proteasome.” J. Biol. Chem 273 (1998): 857-862.
Hagemann M, Wolfel L, and Kruger B. “Alterations of protein synthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 after a salt shock.” J. Gen. Microbiol 136(1990): 1393-1399.
Laemmli UK. “Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.” Nature 227(1970): 680-685.
Ning SB, Guo HL, Wang L, and Song YC. “Salt stress induced programmed cell death in prokaryotic organism Anabaena.” J. Appl. Microbiol 93 (2002): 15-28.
Ornstein L. “Disc Electrophoresis 1, background and theory.” Ann. New York Acad. Sci 121 (1964): 321-349.
Parker R, Flowers TJ, Moor AL, and Harphan NVJ. “An accurate and reproducible method for proteome profiling of the effects of stress in rice leaf lamina.” J. Exp. Bot 57 (2006): 1109-1118.
Rai A and Rai AK. “Morphological and molecular characterization of two usar soil cyanobacterial isolates.” Journal of Scientific and Applied Research 2(2011): 136 - 141.
Sazuka T, Yamaguchi M, and Ohara O. “Cyano2 base updated: linkage of 234 protein spots to corresponding genes through N terminal microsequencing.” Electrophoresis 20(1999): 2160-2171.
Stadtman ER. “Oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins by radiolysis and by metal-catalyzed reactions.” Ann. Rev. Biochem 62 (1993): 797-821.
Tester M, and Davenport R. “Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants.” Ann. Bot 91 (2003), 503-527.
Vinnemeier J, Kunert A, and Hagemann M. “Transcriptional analysis of the isiAB operon in salt-stressed cells of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.” FEMS Microbiol. Lett 169 (1998): 323-330.
Vogel JL, Parsell DA, and Lindquist S. “Heat-shock proteins Hsp104 and Hsp70 reactivate mRNA splicing after heat inactivation. Curr. Biol 5 (1995): 306-317.
Wagner MA, Eschenbrenner M, Horn TA, Kraycer JA, Mujer CV, Hagius S, et al. “Global analysis of the Brucella melitensis proteome: Identification of proteins expressed in laboratory-grown culture.” Proteomics, 2(2002): 1047-1060.
Weber K and Osborn M. “The Reliability of Molecular Weight Determinations by Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis.” J. Biol. Chem 244 (1969): 4406-4412.
Yan S, Tang Z, Su W, and Sun W. “Proteomic analysis of salt stress-responsive proteins in rice root.” Proteomics 5 (2005): 235-244.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21746/aps.2018.7.3.11
Copyright (c) 2018 Annals of Plant Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.


